 Pune City: A Glorious City
Pune City: A Glorious City
Nestled in the western state of Maharashtra, Pune, often referred to as the "Oxford of the East" or the "Cultural Capital of Maharashtra," is a city that beautifully blends history, tradition, and modernity. This vibrant metropolis boasts a rich historical legacy, a diverse geography, and an abundance of historical treasures that make it a fascinating destination for both tourists and history enthusiasts.
Origins and Early History
Pune's origin dates back to ancient times, with evidence of human settlement in the area dating as far back as the 8th century. The city's name is believed to have been derived from the Sanskrit word "Punya," which means "virtuous" or "holy," owing to its spiritual and cultural significance. Throughout history, Pune has been ruled by various dynasties, including the Rashtrakutas and Yadavas, before it came under the control of the Marathas in the 17th century.
Historical Significance
-
The Maratha Empire : Pune played a pivotal role in the rise of the Maratha Empire, thanks to the legendary Maratha king, Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, who made it his capital in 1674. The city served as the epicenter of Maratha power for several decades, witnessing numerous historic events and battles.
-
British Rule : During the British colonial era, Pune continued to be a significant center of administration and education. The city became a prominent hub for social and political reform movements in India, including the freedom struggle against British rule. Many historical sites in Pune bear witness to this period of resistance and change.
Geography and Climate
Pune is strategically located on the leeward side of the Western Ghats, giving it a unique geography characterized by rolling hills, lush greenery, and a pleasant climate. The city enjoys a tropical wet and dry climate, with distinct seasons. The monsoon season from June to September brings much-needed rain, rejuvenating the surrounding landscapes. The moderate climate makes Pune an ideal destination for year-round visits. Here are some key aspects of the geographical importance of Pune:
-
Western Ghats and Sahyadri Mountains: Pune is located at the foothills of the Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri Mountains. These mountains not only add to the city's scenic beauty but also play a crucial role in regulating the region's climate. The Western Ghats act as a barrier, influencing the monsoon patterns and contributing to the city's moderate and pleasant climate.
-
Confluence of Rivers: Pune is situated at the confluence of the Mula and Mutha rivers, which eventually merge into the Bhima River. These rivers not only provide a source of freshwater for the city but also have historical significance, as they were often used for trade and transportation in ancient times.
-
Strategic Location: Pune's location has historically been of strategic importance due to its proximity to the Arabian Sea and the Deccan Plateau. This made it a crucial center for trade and commerce, as well as a military stronghold during various periods of Indian history.
-
Educational Hub: Pune's geographical location has contributed to its emergence as an educational hub. Its proximity to Mumbai, India's financial capital, has attracted students and professionals from all over India and beyond. The city's moderate climate also adds to its appeal as a preferred destination for higher education.
-
Agricultural Significance: The fertile land in and around Pune makes it an important agricultural region. The region is known for its production of various crops, including sugarcane, wheat, and fruits like strawberries. The agriculture sector plays a significant role in the local economy.
-
Tourism: The diverse geography of Pune, with its hills, forests, and rivers, makes it a popular destination for eco-tourism and adventure activities such as trekking and camping. Tourists flock to Pune to explore the natural beauty of the Western Ghats and enjoy the moderate climate.
-
Technology and Industry: Pune's geographical location, coupled with its proximity to Mumbai and the port city of Mumbai, has made it an attractive destination for industries. The city has emerged as a prominent IT and manufacturing hub in India, further boosting its economic significance.
-
Transportation Hub: Pune's location has made it a transportation hub with excellent road, rail, and air connectivity. The Pune International Airport connects the city to major domestic and international destinations, facilitating trade and tourism.
Historical Places of Pune
Pune is dotted with historical landmarks that offer a glimpse into its glorious past. Some of the must-visit historical places in Pune include:
Shaniwar Wada : Built in the 18th century, Shaniwar Wada is a majestic fort palace that was the seat of the Peshwa rulers of the Maratha Empire. Despite the devastating fire that destroyed parts of it, the palace remains a symbol of Pune's rich history.
Aga Khan Palace : This iconic palace was built in 1892 and is famous for its association with Mahatma Gandhi. It served as a prison for him and other freedom fighters during the Quit India Movement. Today, it houses a museum dedicated to the life and work of Gandhi.
Sinhagad Fort : Perched atop a hill, Sinhagad Fort offers breathtaking views of the Sahyadri Mountains. It has played a crucial role in the history of the Marathas and is a popular trekking destination.
Raja Dinkar Kelkar Museum : Named after its founder, Dr. Dinkar Kelkar, this museum houses an impressive collection of artifacts and artworks, showcasing the rich cultural heritage of India.
Lal Mahal : The Lal Mahal is a reconstructed palace that once served as the residence of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj. It is a significant historical site and an excellent place to learn about the Maratha history.
Parvati Hill and Temple: Parvati Hill is a scenic spot in Pune with a historic temple complex dedicated to the goddess Parvati. The hill offers stunning views of the city and is a popular destination for both tourists and locals.
Dagdusheth Halwai Ganpati Temple: This revered temple is dedicated to Lord Ganesha, the elephant-headed deity, and is known for its grand celebrations during the Ganesh Chaturthi festival. It is one of the most visited religious sites in Pune.
Pataleshwar Cave Temple: This rock-cut temple, dating back to the 8th century, is dedicated to Lord Shiva. It is renowned for its unique architectural style and the peaceful atmosphere it offers within the bustling city.
Vishrambaug Wada: This historical mansion was built in the early 19th century and showcases traditional Marathi architecture. It is a fine example of the residences of the Peshwas and now houses a museum.
Katraj Snake Park and Zoo: Located on the outskirts of Pune, this park is home to a variety of reptiles and is a great place for families and wildlife enthusiasts to learn about and observe these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion : Pune, with its deep-rooted history, diverse geography, and wealth of historical sites, stands as a testament to India's rich and dynamic heritage. Whether you're a history enthusiast, a nature lover, or simply seeking a vibrant cultural experience, Pune has something unique to offer. It continues to thrive as a modern city while honoring its historical legacy, making it a truly remarkable destination in Maharashtra.
Major City & Locations of Pune
Pune District is a prominent district located in the western state of Maharashtra, India. It is known for its rich history, cultural heritage, educational institutions, and industrial development. Here are some important and major locations in Pune District:
-
Pune City: The district headquarters and one of the most significant cities in Maharashtra. Pune is famous for its educational institutions, including the University of Pune, and is often referred to as the "Oxford of the East." It is also an industrial and IT hub.
-
Koregaon Park: A posh locality in Pune known for its upscale residential areas, restaurants, cafes, and shopping centers.
-
Shivajinagar: A central area in Pune with government offices, educational institutions, and commercial complexes.
-
Kothrud: A prominent residential and educational area in Pune, known for its quality schools and colleges.
-
Hinjawadi: An IT park and technology hub located in the western part of Pune, home to numerous IT companies and tech parks.
-
Aundh: A residential and commercial area in Pune known for its modern infrastructure and shopping centers.
-
Viman Nagar: Located near Pune Airport, it is a rapidly developing area with residential and commercial spaces.
-
Deccan Gymkhana: A historic area in Pune known for its cultural institutions, including the Deccan College and Fergusson College.
-
Hadapsar: An industrial and residential suburb in eastern Pune, known for its industrial estates and IT companies.
-
Sinhagad Fort: A historic hill fort located southwest of Pune, offering panoramic views of the city and significant historical importance.
-
Alandi: A town located on the banks of the Indrayani River, known for the Saint Dnyaneshwar Alandi Temple, an important pilgrimage site for devotees.
-
Jejuri: A town famous for the Khandoba Temple and the annual Jejuri Yatra, attracting a large number of devotees.
-
Lonavala and Khandala: Hill stations located in the Pune District, known for their scenic beauty, waterfalls, and trekking spots.
-
Mulshi: A picturesque region with a beautiful reservoir, ideal for nature enthusiasts and adventure seekers.
-
Lavasa: A planned hill city and tourist destination with European-style architecture, situated near Pune.
-
Bhuleshwar Temple: A historic temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, known for its unique architecture, located near Yawat.
These are some of the important and major locations in Pune District, each offering its own distinct charm and significance.
Development Authorities in Pune
Pune, being one of India's major cities, has seen rapid urbanization and growth over the years. To manage this development in an organized and sustainable manner, various development authorities and agencies have been established. These entities work together to create and implement a Master Plan for Pune to guide its growth and development. Here's an overview of the development authorities in Pune and the city's Master Plan:
-
Pune Municipal Corporation (PMC): PMC is the local governing body responsible for the administration of Pune city. It plays a vital role in the city's urban development, including the provision of civic amenities, infrastructure, and urban services. PMC is involved in land-use planning, issuing building permits, and maintaining the city's infrastructure.
-
Pune Smart City Development Corporation Limited (PSCDCL): Pune Smart City Development Corporation Limited was formed as part of the Smart Cities Mission initiated by the Government of India. PSCDCL focuses on implementing smart city projects aimed at enhancing the quality of life for Pune's residents through technology-driven solutions.
-
Pune Metropolitan Region Development Authority (PMRDA): PMRDA is a key planning and development authority responsible for the Pune Metropolitan Region. It was established to ensure coordinated and planned development in the region, which includes Pune city and its surrounding areas. PMRDA plays a crucial role in infrastructure development, land-use planning, and addressing urbanization challenges in the metropolitan region.
The Pune Metropolitan Region Development Authority (PMRDA) is a significant governmental organization responsible for the planned and sustainable development of the Pune Metropolitan Region (PMR) in the Indian state of Maharashtra. Established in 2015, PMRDA has been instrumental in addressing the urbanization challenges faced by the Pune region, one of India's fastest-growing and economically vibrant areas.
Here are some key aspects of the Pune Metropolitan Region Development Authority (PMRDA):
-
Formation and Objectives: PMRDA was established with the primary goal of promoting balanced regional development in and around Pune. The authority was formed under the Maharashtra Regional and Town Planning Act, 1966, to create a comprehensive and integrated approach to urban development, infrastructure, and transportation planning within the Pune Metropolitan Region.
-
Jurisdiction: PMRDA's jurisdiction extends over an area that encompasses not only the Pune Municipal Corporation (PMC) but also the surrounding municipalities, towns, and villages. This expansive jurisdiction enables PMRDA to plan for the entire region's development, ensuring that growth is coordinated and sustainable.
-
Development Plans: PMRDA plays a pivotal role in formulating and implementing development plans, land use policies, and infrastructure projects within the Pune Metropolitan Region. These plans aim to accommodate the region's burgeoning population, improve transportation networks, and provide essential amenities like housing, water supply, and sanitation.
-
Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure development is a crucial aspect of PMRDA's responsibilities. The authority oversees the construction and maintenance of roads, bridges, public transportation systems, water supply, sewage treatment plants, and other essential infrastructure components. This focus on infrastructure aims to enhance the quality of life for residents and promote industrial and commercial growth.
-
Transportation Planning: PMRDA is actively involved in transportation planning and execution. It works on the expansion and improvement of road networks, metro rail projects, and other forms of public transportation to ease traffic congestion and provide efficient mobility solutions for the region's residents.
-
Environment and Sustainability: In recognition of the need for sustainable development, PMRDA places a strong emphasis on environmental conservation and sustainable practices. This includes green initiatives, waste management, and the preservation of natural resources.
-
Economic Development: PMRDA actively encourages economic development in the Pune Metropolitan Region. It fosters an environment conducive to businesses, industries, and investment, which contributes to job creation and economic growth.
-
Smart City Initiatives: PMRDA is also involved in smart city initiatives, leveraging technology to enhance the quality of life, improve governance, and create a more connected and efficient urban environment.
-
Public Engagement and Collaboration: PMRDA engages with the local community, stakeholders, and experts to gather input and ensure that development plans are inclusive and meet the needs of the people. Collaboration with various government departments and agencies is also a key aspect of its functioning.
-
Challenges and Future Directions: Like many rapidly growing urban areas, the Pune Metropolitan Region faces challenges such as traffic congestion, environmental sustainability, and housing shortages. PMRDA's future efforts will likely focus on addressing these issues while continuing to promote the region's economic and social development.
The Pune Metropolitan Region Development Authority (PMRDA) plays a vital role in shaping the future of Pune and its surrounding areas. Through strategic planning, infrastructure development, and a commitment to sustainable practices, PMRDA aims to create a thriving and well-connected metropolitan region that offers a high quality of life for its residents and attracts investment and opportunities for growth.
Master Plan of Pune : The Master Plan of Pune, often referred to as the Development Plan (DP), is a comprehensive planning document that outlines the city's future growth and development strategies. The Master Plan typically covers various aspects of urban planning, including land-use zoning, transportation, infrastructure, housing, environment, and economic development. Here's an overview of the Master Plan's key components:
 |
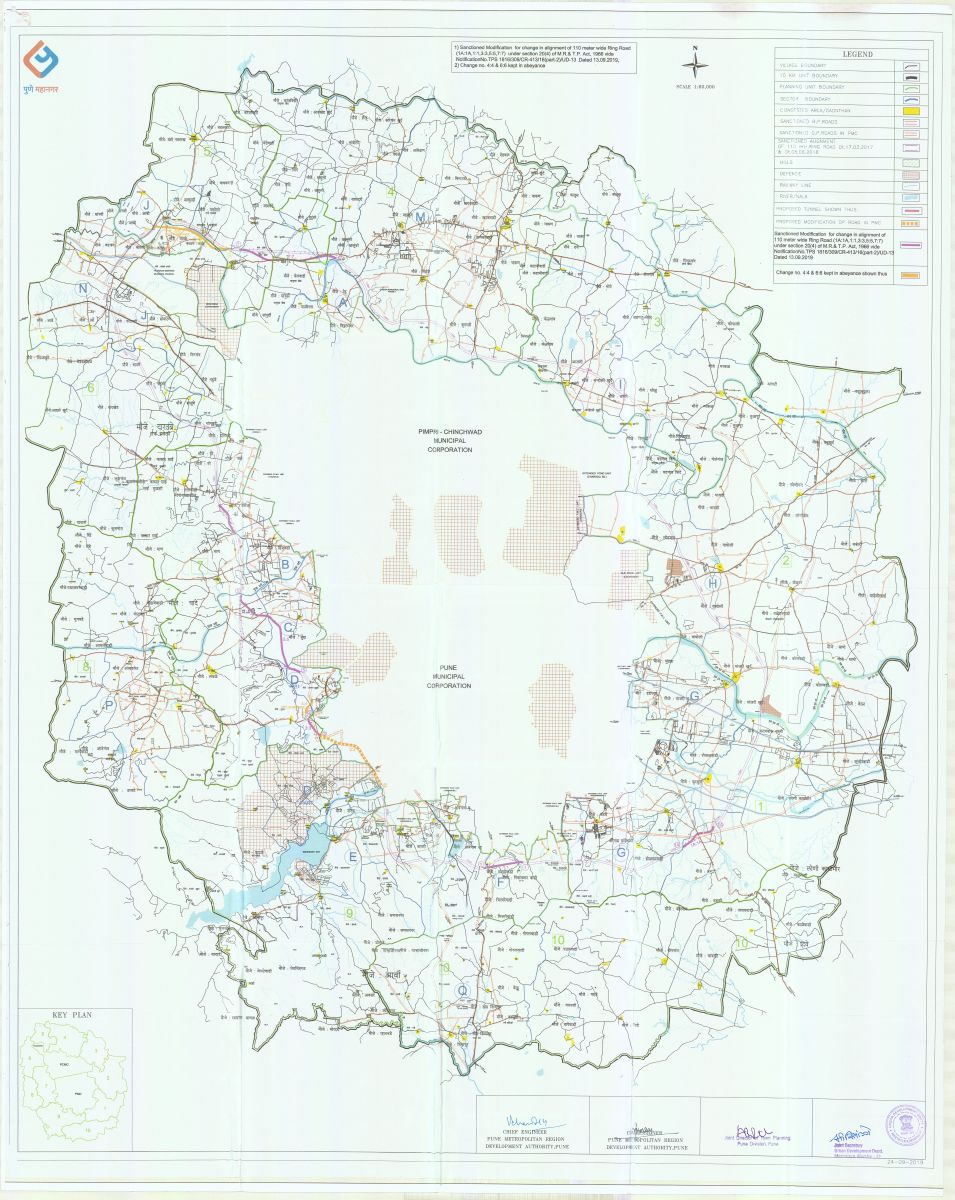 |
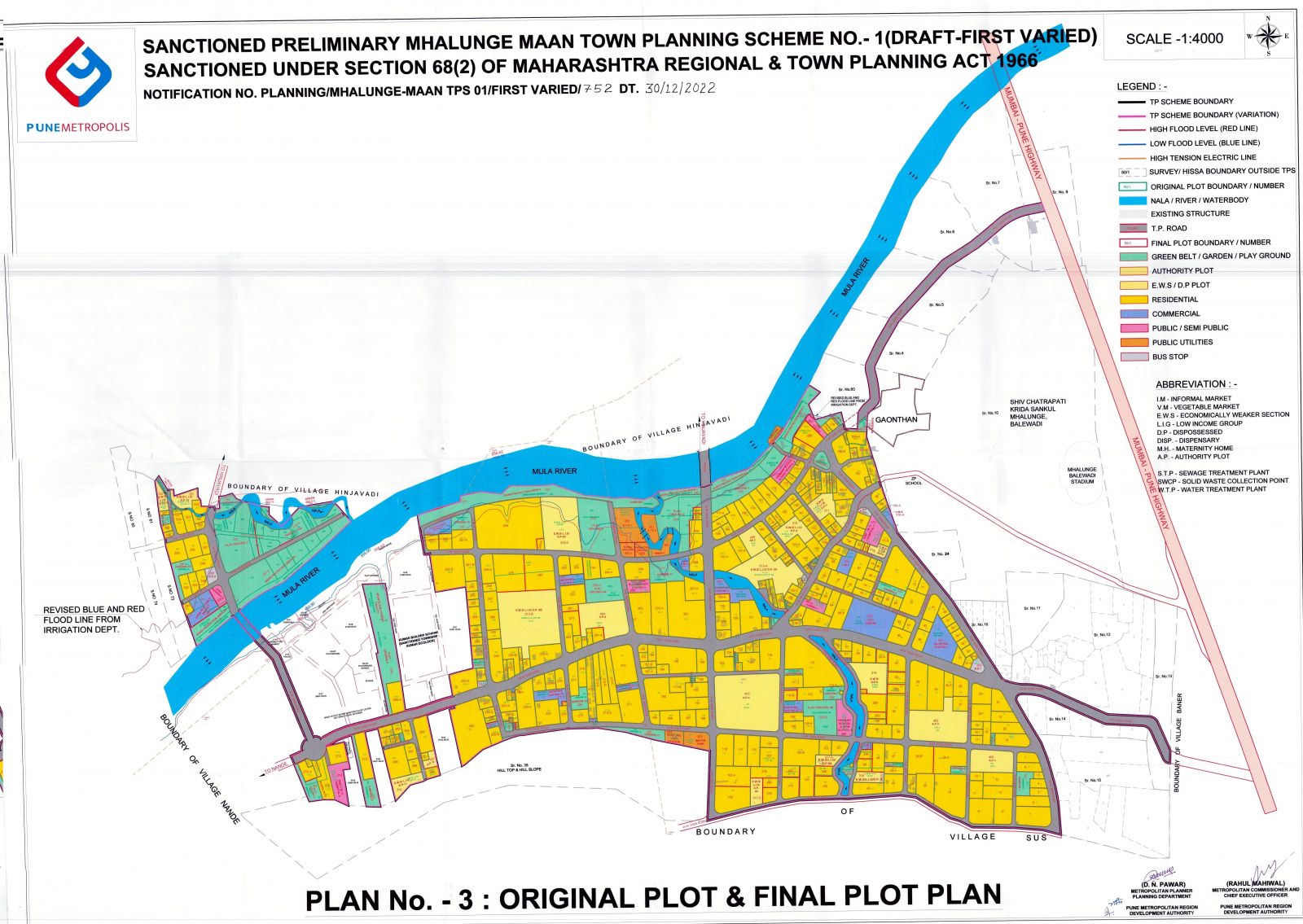 |
| HOLKARWADI TPS 5 | Ringroad-min | Map 3 |
 |
_page-0001-min.jpg) |
 |
| HOLKARWADI TPS 4 | PRELIMINARY_SCHEME_final_dwg-3._OP_FP_PLAN | PMRDA Region |
 |
 |
 |
| Submitted TPS no. 2 Wadachiwadi | Submitted TPS no. 3 Autade Handewadi |
-
Land-Use Zoning: The Master Plan designates specific land-use zones, such as residential, commercial, industrial, recreational, and green spaces. Zoning regulations ensure that land is used efficiently and in line with the city's development goals.
-
Transportation and Infrastructure: It outlines strategies for improving transportation networks, including roads, public transit, and infrastructure projects like bridges and flyovers. The goal is to enhance connectivity and reduce traffic congestion.
-
Housing and Urban Development: The plan addresses housing needs, affordable housing initiatives, and strategies for improving the quality of housing in the city. It also promotes sustainable and inclusive urban development.
-
Environment and Sustainability: Master Plans incorporate environmental considerations, such as green spaces, parks, and conservation areas, to balance development with environmental preservation.
-
Economic Development: Strategies for fostering economic growth, promoting industries, and creating employment opportunities are included in the plan. It often identifies growth corridors and industrial zones.
-
Social Infrastructure: The plan includes provisions for educational institutions, healthcare facilities, recreational areas, and other social amenities to cater to the needs of the growing population.
-
Implementation Mechanisms: The Master Plan outlines the steps and mechanisms for its implementation, including regulatory measures, public-private partnerships, and funding sources.















Leave a Comment